My hand trembled as I typed the title. I’m not sure if I can explain it well enough. We can. We’ll handle it together.
From now on, I plan to link my articles about devices here. For this reason, I must summarize it properly.
Do you think I will go to Mars in the rest of the article or will I make my sister-in-law jealous?
Definition : Let’s start with a simple definition. A mechanical or electronic device made for a specific purpose.
When you think of a device as a perception, you think of something that has cables, works with electricity and has the capacity to make beeping sounds. It’s not really wrong, but a coffee grinder is also a device. Let’s not limit ourselves.
Focus on purpose and usage words. We have a purpose and we use something to achieve it. The same definition we gave in our user article.
From the point of view of the user experience designer, we are the people who develop this device in terms of
- Usability
- Usefulness
- Desirability
and support the users.
Which Devices?
We are not living at the end of the Paleolithic era, in the year 10,000 BC. If it were, we would say stone, stick, ivory needle, staghorn spear, and most of our work would be done.
Now we have thousands of different kinds of devices. So let alone listing them all, we probably won’t even know about many of them. So let’s examine the most used ones and those that make sense in terms of experience design. For now, I’ll go over the major electronics that are the subject of user experience.
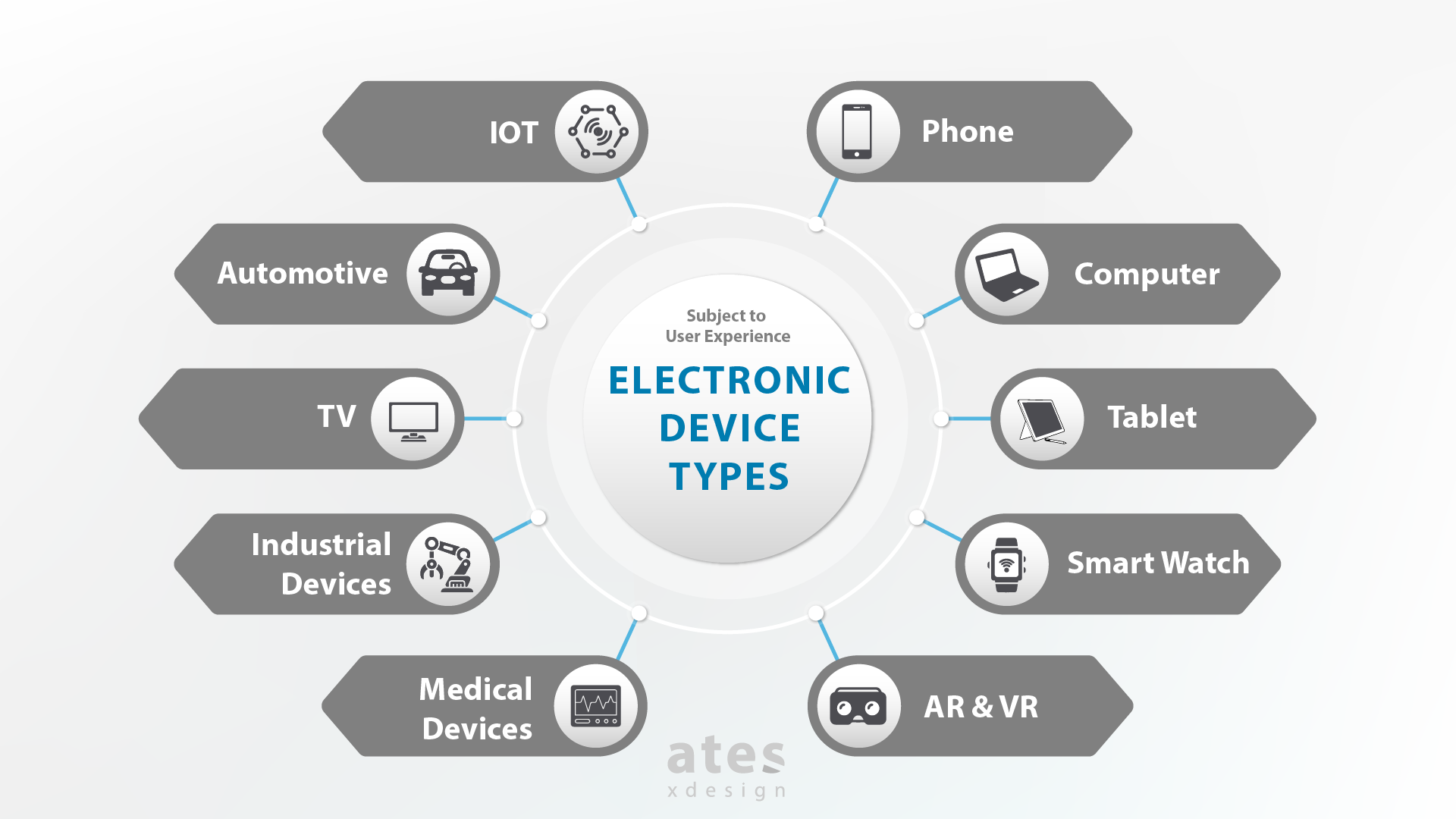
Phone : It is the primary device in experience design as it has billions of users (5.2 Billion non-unique subscribers ), including the homeless. It is always with us and has revolutionized and even changed the use of the internet. The computer software we are accustomed to continues to exist with versions suitable for the small and touch screen of the phone.
Computer : Due to its speed and scope, it is a device that is still very heavily used as laptops and desktops. There hasn’t been a significant change in their forms for years. For this reason, we can say that user experience studies are carried out by keeping the software in the foreground.
Tablet : It was created when there is a need for a device that we can easily carry with us, such as a phone, but with a large screen. It is not as common as a phone or computer, but it has recently attracted attention with its very fast, very capable (and of course very expensive) versions.
Almost all websites and most of the applications are designed in accordance with the phone, tablet and computer trilogy. Thus, the experience of all possible users is taken into account. If you haven’t heard the word Responsive Design, I suggest you do your research.
Smart Watch : They are the devices produced as an answer to the question of how far we can go in carrying technology with us. For some reason, they are cute to everyone, but the number of active users is few. Because they are both very small and slow. Its software has been developed mostly for sports and health, which is very suitable for use.
AR & VR : Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality devices are devices that pull you into a virtual but realistic world to make you feel as if you are away from the screen and your environment. Efforts are made to provide a real-world experience for this computer-generated world.
Internet of Things (IoT) : It refers to all devices connected to each other and to the Internet. The difference is that the connected device can be any electronic device. Refrigerators, irons, air conditioners and similar products can connect to the internet, whatever comes to mind. What matters is whether he has something to say or listen to during this connection. Smart home systems are the most common area of use, but they have an almost unlimited range of uses.
Automotive : Of course, there is a mass among us who do not see cars without screens. They may not have felt this development. But now almost all cars have their own computers, map and navigation software, music and movie players. In summary, there is a screen and software in the car. If you consider the limited mobility of the person driving in the seat, you can see that there is a very important improvement area in terms of user experience.
Television : For some reason, I didn’t want to write television at first. But since smart TVs contain both screen and software, we can see them as an important device in terms of user experience. So why do I feel lost (in a bad sense) even on the best smart TV? Anyone using Netflix or Amazon Prime and going crazy to get the movie they want from the TV remote? It’s up to us to fix it, ladies and gentlemen.
Industrial Devices : You can see it as not the subject of user experience. The number of users is small, so it is not common. But as an engineer, I know how user-oriented errors are in factories and production environments. I also know that the cost of a small mistake is insane. For this reason, I can clearly say that every device that works in the industrial field, has a screen and software is the subject of experience design.
Medical Devices : If you are using a health-related device, a person’s life may be at stake. Even if his life is not endangered, it may be for his health in the short or long term. Especially in critical periods such as the pandemic period, when it is very difficult to focus the attention of healthcare professionals and ensure that they use everything correctly. Then we need to carefully examine the screens, software and buttons.
You can think of dozens of different devices that I have not categorized here. For example, kiosks. But kiosks can be accepted in the category of computers, tablets and even televisions. That’s why we don’t write everything down, but we don’t forget about it either.
Oh, and I kept repeating the screen, but in fact, the user experience is extremely important on devices without a screen. Like the steering wheel of a car. I cannot ignore this. Let’s take an extreme example. Robots. They look like autonomous devices, but they are devices that you use for a purpose. Many do not have screens. It would be naive to think that robots are not the subject of experience design. (The robot in the photo below has a screen. But I put it because it’s cute.)
Components of the Device
Electronic devices are examined in two separate sections as hardware and software. Both are the subject of experience design. Experience studies are carried out for both the physical features and ergonomics of the device and the ease of use of the software inside.
Hardware
It refers to the physical part of electronic devices that can be held and seen. Like mobile phone case, screen, camera, buttons and all other parts inside the case. Let’s continue with the mobile phone.
The general structure of the equipment is designed in accordance with human ergonomics. In other words, having an easy-to-hold, easy-to-see, easy-to-press button/screen, and easy-to-pocket phone are already indispensable rules. Then you develop its technical characteristics. E.g;
- Instead of 8 Megapixels, you put an 800 Megapixel (no such thing yet) camera. But you make sure it doesn’t come out of the phone’s case.
- You ensure that the phone does not consume much battery.
- You ensure that it has a processor powerful enough to run new applications.
- You ensure that it is compatible with 5G, 6G, 10G to provide the fastest internet experience.
- You ensure that it has an unbreakable screen that can give brilliant images in high resolution.
- You ensure that it has a gold-colored case with pink polka dots, but that looks different colors from different angles.
- You ensure that your users have a memory large enough to fit the 36,876 photos they took while on vacation in Bahama.
- You make the phone have laser beams with which it can see through walls and destroy tanks.
- You put everything inside the phone and make it as light as a feather.
- On top of that, you make it all cheap.
Of course, you cannot achieve everything that is imagined together. In order not to lose customers, you combine these features in different combinations and produce different models. You get a lot of models that are cheap (affordable), little expensive, expensive, very expensive, shockingly expensive. People are confused about what to choose. But they still choose. Because the sister-in-law, with whom she did not get along very well, bought a sub-model of that phone (I will tell you about this psychology later).
You have built a device powerful enough to go to Mars, but are you aware that the decision to buy was made based on sister-in-law?
Software
These are the programs in the electronic device to perform its functions in the background and to interact with you. Low-end software that functions among the hardware itself is not our topic. But in the foreground, that is, the software that you are in direct contact with and that you use constantly is very important;
- Operating System : It is system software that manages the hardware of the device you are using and acts as a shell for all other software (like applications) to run in it. The important ones are;
- Mobile (All portable devices)
- Android
- iOS
- Windows
- iPadOS
- WatchOS
- Wear OS
- Tizen
- Personal Computers
- Windows
- MacOS
- Linux
- Chrome OS
- Mobile (All portable devices)
- Web Browser : It is the basic software that allows you to surf the Internet. When you enter a website address starting with www or click on the red bag campaign link sent by a friend, this software compiles the information on the website from the server and brings it to you visually. Most used browsers (descending sort);
- Chrome
- Safari
- Internet Explorer
- Samsung Internet
- Edge
- Firefox
- Applications : They are software designed to perform a specific task. Excel on your computer is also an application, Instagram on your mobile phone is an application. Candy Crush Saga is also an application. It is a more used term in the mobile phone world and is also known as App.
So What?
The device can be the tool that connects your user with your products and services, or it can be your actual product itself. In any case, it’s one of the things that most impacts your user’s experience. That’s why you need to be aware of the design, ergonomics and software of the devices.
If you intend to design or improve the user experience on your website or application, you must know the devices that are most used among your users at that time. Phones, computers, tablets; their screen sizes and resolutions; web browsers running in… Knowing these is very important for you to improve the experience.
Obtaining this information is not easy. My first suggestion is to review your own website’s statistics (for example, via Google Analytics). From here, data about both the devices used by your users and their basic software can be obtained. Very professional and very expensive UX software is also available. They generate data that is exaggerated enough to map out the street where people entering your website played games as a kid. It is up to you to interpret these data.
You should also be following the industry, news and current technologies. However, it should be noted that the most sold phone today is not actually the most used phone today. You should know that phones sold 1-2 years ago are more widely used. You should be aware that resolution and viewport area are different things and it is an issue that directly affects everything displayed on the screen etc.
The best-selling phone today is not the most used phone today.
A Real Example
We needed to make an important mobile application that would reach several million people. It was very important that it was error-free, as television commercials would be broadcast shortly after the application went live.
First, we made a list of the most used phones in Turkey. We examined the screen resolutions, operating systems and web browsers of these phones and designed the application accordingly. It was not possible for us to use screen design or compatible software suitable for all devices of all users. For this reason, we identified the most used ones and disabled the 1-2 phones in the bottom row.
For example, we had to reduce some features of the application in order to release it that is compatible with iPhone 4s screen sizes and operating system. When we checked, we found that only 3% of people who visit our website use iPhone 4s. Considering that other phones (97%) were quite adequate, we preferred to release the application with rich features.
Of course, while doing these, we also took into account the developments we will make throughout the year and the future compatibility of the infrastructure we will use in the present. We recruited and trained new personnel according to the development speed of the project.
Since it is a unique application in Turkey, we have created content that people can understand in the best way without being surprised.
We had dozens of test devices and many detail-oriented friends on duty just for the test processes. Before the device tests, we tested exactly what was displayed on the screens of the devices and the efficiency of the flow with simulators.
We also worked with a design agency that specializes in UX (User Experience) for screen designs. Sometimes we had a long discussion with 5 people about the shape, position, size, color and text of a button on the screen. Because that button was perhaps the button that would lead us to success.
Trust me, everyone on our team would love to work more on the staghorn spear. But that was 12,000 years ago. We design today.
References :
User experience design, Wikipedia
Operating system, Wikipedia
Paleolithic Technology, Culture and Art (Turkish), Khan Academy
Miscellaneous statistical information, www.statista.com
Miscellaneous statistical information,www.statcounter.com

Ates Evren Aydinel
Engineer. 22 years white collar. Financial digital projects manager. Guest lecturer at various universities and institutions. Consultant. Book writer and publisher. Founder of Ates Experience Design.


